Educational programme
MRBS’s educational programme consists in:
- 3 Hands-on modules ( each consisting of 3-day training courses held throughout the first year).
- 9 on-line modules followed by a Tutoring session each held throughout the 2 academic years
- The clinical immersion programme consists of 3 modules, to be held at one of our accredited training centers (a minimum of 6 weeks and a maximum of 12 months).
- An online module to develop the methodological aspects of clinical research finished with the presentation of a Master Thesis.
- A final exam.
To be awarded this Lifelong Learning Master’s Degree issued by the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, trainees must complete the educational programme: pass all the modules, pass the practical assessment, do the minimal period of clinical immersion and present a research project.
Basic Sciences on breast disease:
- How to build a breast unit
- Breast cancer research: How, who and when
- Imaging Techniques for breast:
Ultrasound. Mammogram. MR imaging. Breast PET Scan for diagnosis and follow-up.
Interventional radiology: stereotactic breast biopsy, imaging-guided needle breast biopsy, ultrasound guided breast biopsy
Benign breast disease:
- Nipple discharge and the role of ductoscopy
- Inflammatory and related lesions: mastitis, foreign body reactions, recurrent subareolar abscess, mammary duct ectasia, fat necrosis
- Fibrocystic changes: cysts, adenosis, metaplasia, epithelial hyperplasia, ductal lesions, lobular lesions, columnar cell lesions, radial scar and complex sclerosing lesion, intraductal papilloma and papillomatosis
- Benign tumours: fibroadenoma, lipoma, adenoma, hamartoma, granular cell tumour

Management of malignant breast disease:
- Diagnosis of breast cancer:
Clinical examination / Laboratory investigations / Pathological diagnosis / Clinical staging and risk assessment / Prognostic factors - Treatment:
Adjuvant systemic therapy / Primary chemotherapy (neoadjuvant chemotherapy) in locally advanced breast cancer / Follow-up - Management of metastatic disease:
Staging of metastatic or recurrent breast cancer / Local recurrence / Systemic dissemination / Chemotherapy regimens for recurrent or metastatic breast cancer
- Pathological handling of breast cancer excision specimens:
Fine needle aspiration biopsy and core needle biopsy / Mastectomy specimen / Mammographically-directed excisions / Frozen section diagnosis / Surgical pathology report of breast cancer specimens. - Radiotherapy guidelines for breast cancer:
Radiotherapy for ductal carcinoma in situ / Criteria for breast conserving therapy / Post-mastectomy radiotherapy / Radiotherapy after pre-operative systemic therapy. - Management of special situations in breast cancer:
Breast cancer in elderly women / Breast cancer in very young woman / Breast cancer in male.
Surgical anatomy of the breast
Breast conserving surgery:
- Tumorectomy
- Quadrantectomy
Techniques of mastectomy:
- Simple mastectomy
- Skin sparing
- Nipple sparing
- The axilla
Current management / Sentinel node biopsy / Lynmphedema prevention - Partial breast reconstruction
Oncoplastic surgery techniques for breast conserving surgery:
- Local perforator flaps: TDAP, ICAP, LICAP, SEAP…
- Autologous platelet gel prosthesis to fill tumorectomy defect.
- Fat grafting

- Locally advanced breast cancer
Oncological surgery management / Chest wall reconstruction - Management of breast cancer sequelae
Shoulder damage / Chronic pain / Radiation induced angiosarcoma / Psychological impact
- Surgical guidelines for breast cancer
Surgical approach to the axilla including sentinel lymph node biopsy / Surgical technique - Psychosocial issues in breast cancer
- Sentinel node biopsy approach in internal mammary chain
- Skin sparing mastectomy
- Axillary lymphnode clearence
- Implant reconstruction with ADM
- Breast Glandular flaps
- Flap dissections:
Latissimus dorsi / DIEP / SGAP / TUG / PAP
Lower limb and pelvis:
- PAP
- Lumbar perforator flap (LPF)
- Inferior gluteal artery perforator flap (IGAP)
- Superior gluteal artery perforator flap (SGAP)
- Gracilis (ATMG)
Trunk:
- Internal mammary fascio-cutaneous flaps
- Intercostal flaps
- Scapulo-dorsal flaps:
Latissimus dorsi / Thoracodorsal artery perforator flap (TDAP) / Scapular flap / Parascapular flap / Chimeric flaps - Abdominal wall flaps:
Musculo-cutaneous rectus abdominis flap (TRAM) / Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap (DIEP) / Taylor, superficial inferior epigastric artery flap (SIEA). - Free lymph node transfer
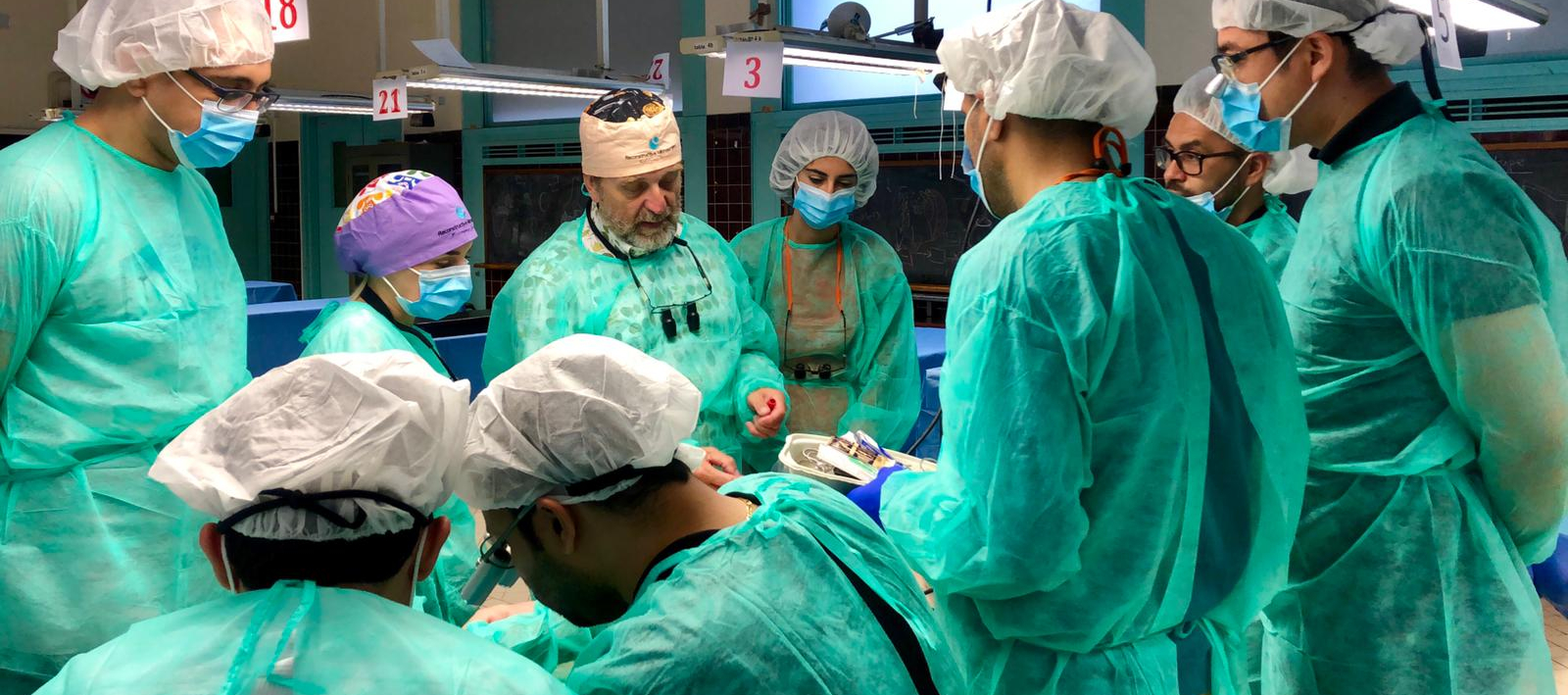
Intensive training course on basic microsurgical skills using a small animal model (rat):
- Basic management of experimental animal, microscope and instrumentation
- End-to-end suture of the carotid artery and femoral artery
- End-to-end suture of the jugular vein and femoral vein
- Aorto-iliac end-to-end suture
- End-to-side suture between femoral artery and vein
- Jugular vein graft to carotid artery
- “In situ” groin flap
- Distant groin flap to the neck
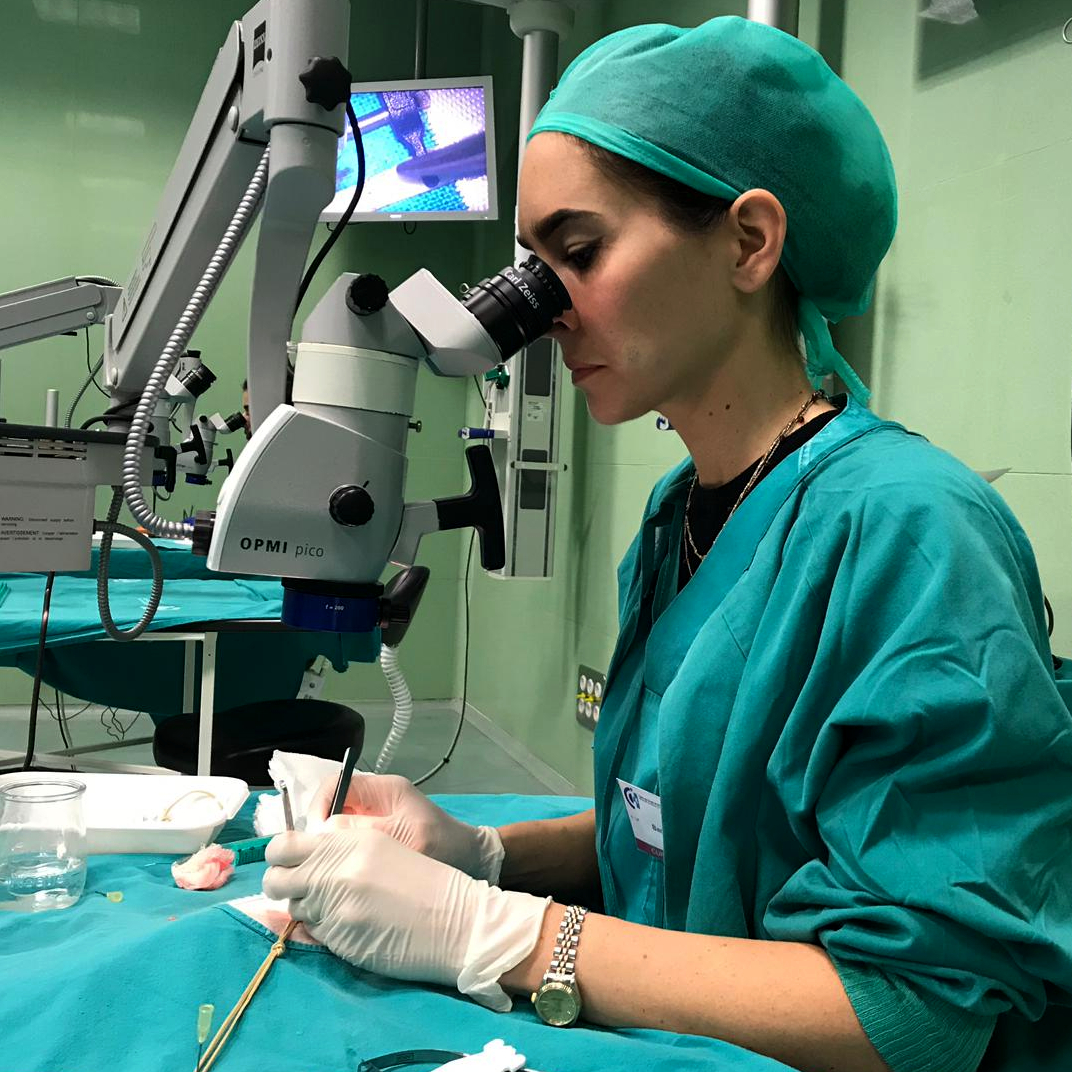
Intensive course on dissection of perforator flaps in live animals (pig) and basic supermicrosurgical skills training:
- Perforator flap anatomy
- Preoperative planning of perforator flaps
- Dissection technique of perforator flaps
- Dissection technique in lymphatic surgery
- Fundamentals of microsurgical techniques
- Perforator Flaps in Breast Reconstruction
- ICT lymphography assessment on pigs
“Hands on” dissection session:
- Gluteal and dorsal perforator flaps.
- Free style perforator flaps.
- Transferring the flaps to the recipient vessels.
- Super microsurgical flaps.
- Lymphatic channel dissection.
- Lymph node transfer
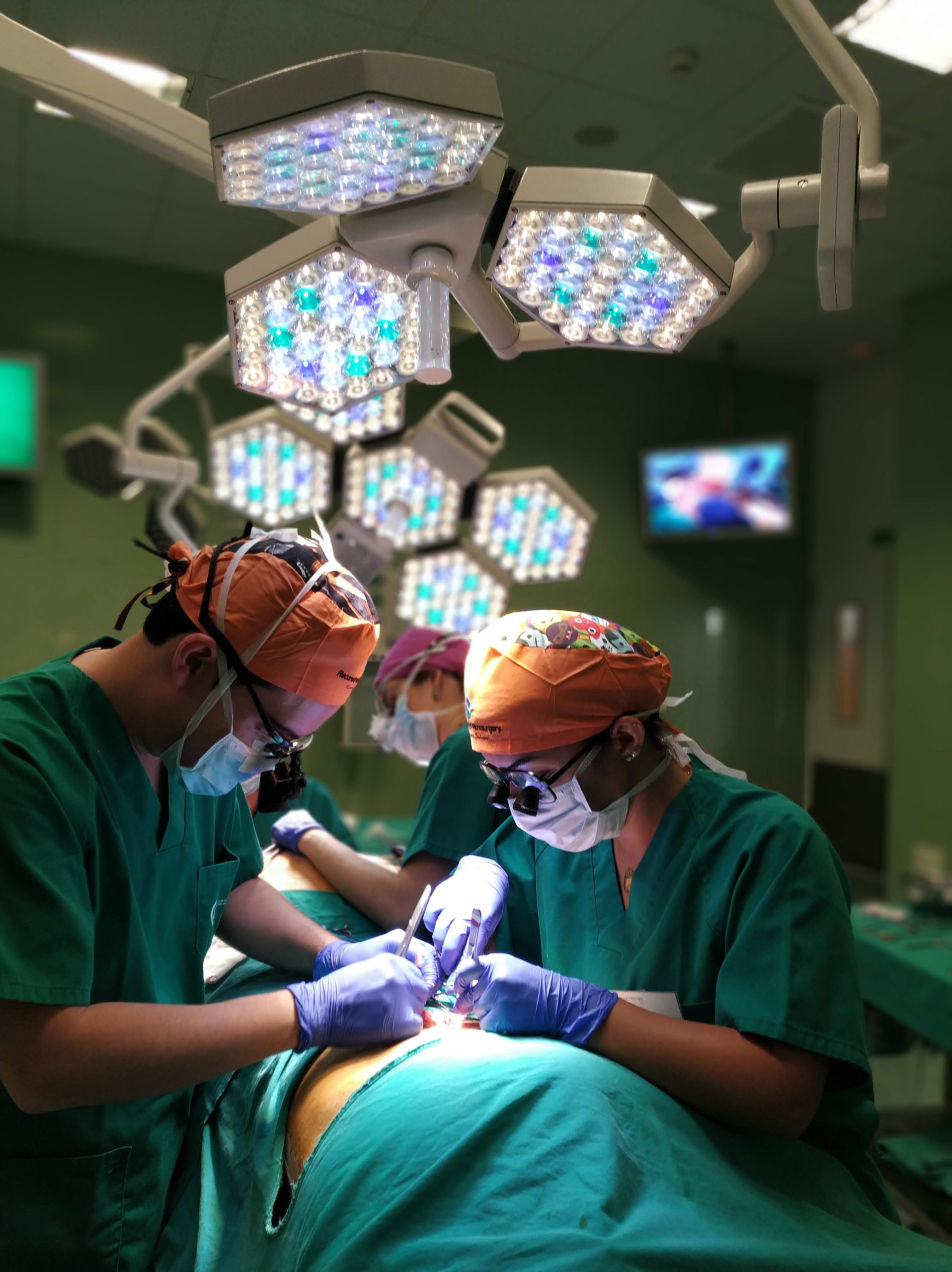
Essential concepts in breast reconstruction:
- The psychological impact.
- Provision of information.
- How to assess and provide options.
- Influence of chemotherapy
- How to setup a breast reconstruction unit
Immediate vs delayed breast reconstruction. Indications and contraindications
High risk breast cancer:
- Genetic breast cancer.
- Identifying women at high risk.
- Prophylactic mastectomy:
Subcutaneous mastectomy / Skin sparing mastectomy / Nipple sparing mastectomy / Nipple-areola sparing mastectomy
Radiotherapy in breast reconstruction:
- Timing post radiotherapy.
- The impact of ADM.
- Post autologous reconstruction
Breast reconstruction in special situations:
- Obese patients
- Skinny patients
- Elderly patients
Primary implant reconstruction:
- How to mark for an SSM
- Two-stage breast reconstruction utilizing tissue expander and implant
- Matrices: biologic vs synthetic, indications, contraindications

Delayed breast reconstruction with Implants:
- Two-stage breast reconstruction utilizing tissue expander and implant
- The role of Becker expander
Composite implant breast reconstruction
Nipple-areola reconstruction
Contralateral breast symmetrisation
Management of complication:
- Capsular Contracture.
- Infection and extrusion in implants based reconstruction.
- Skin flap necrosis.
- Asymmetry.
- Rippling.
- Rotation.
- Malposition
- Litigation in breast surgery
Perforator flaps in breast reconstruction:
- DIEAP / SIEA / SGAP / IGAP / LAP / PAP / extended TDAP
- How to get out of trouble intraoperative
- How to prepare and plan:
Assesment of smoking, diabetes…, prior surgery to harvest site / Imaging in perforator flaps
Postoperative management:
- Flap monitoring
- How to manage complications
Live webcast surgery will also be shown and students’ interactive participation will be encouraged
- Oncological management in breast tumors
- Reconstructive planning in breast tumors
- Breast reconstruction with implant vs autologous tissue reconstruction
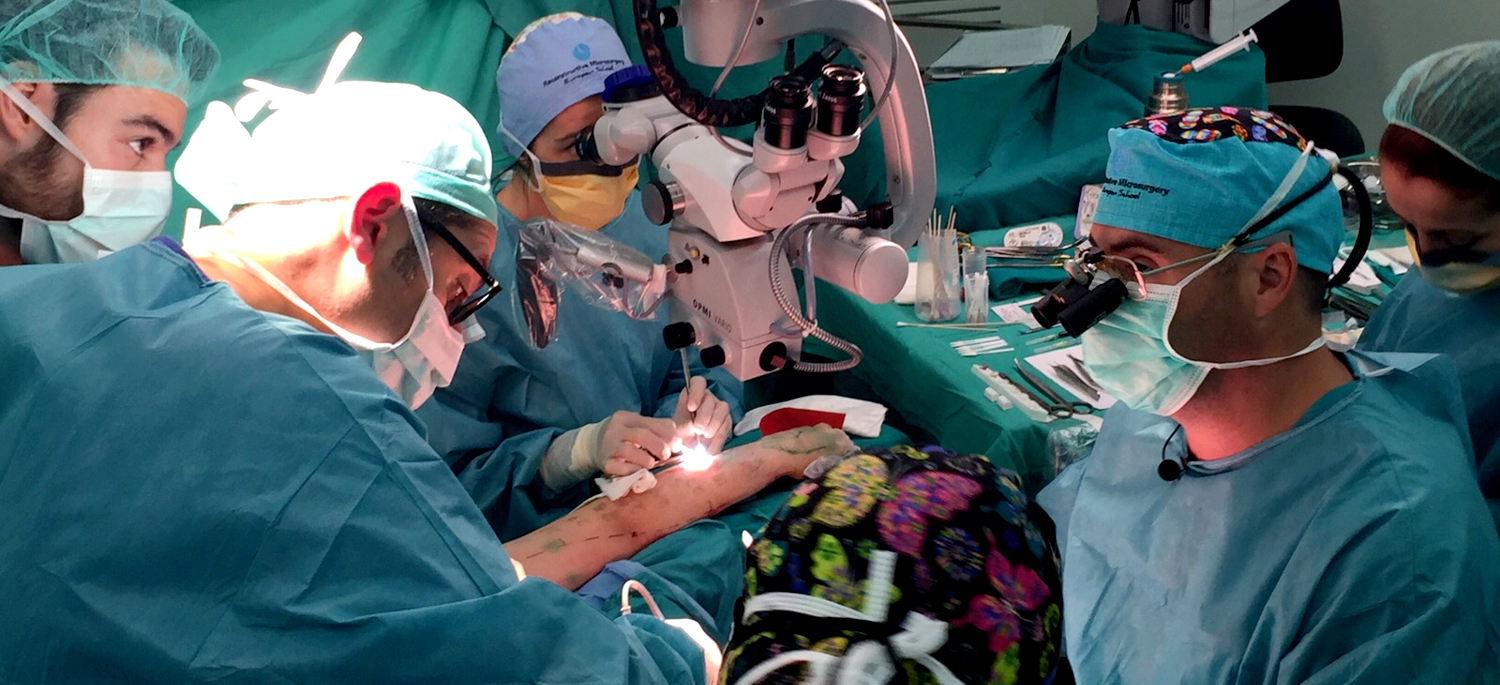
Immediate and delayed reconstruction:
- Oncoplastic breast surgery: glandular and perforator flap techniques.
- Breast reconstruction:
DIEP flap / SIEA flap / TAP flap / SGAP flap / IGAP flap / Fat grafting / Transverse myocutaneous gracilis flap (TMG) / Extended TAP / PAP / Lumbar perforator flap / Latissimus dorsi
.
- Partial breast reconstruction: oncoplastic and perforator flap techniques
- Autologus flap reconstruction with fat grafting
- Thoracic wall reconstruction
Aesthetic concepts of the breast:
- Definitions.
- How to measure the breast.
- Imaging techniques (photography, 3D imaging, etc).
- How to conduct a consultation for an aesthetic breast procedure
Breast Augmentation:
- Implants: types, incisions, plane, complications
- Secondary surgery.
- Fat grafting as adjuvant.
- Imaging diagnostic techniques for follow-up
Breast Reduction Mammoplasty:
- Pre-operatory study
- Techniques: superior pedicle, inferior pedicle, lateral pedicle, round-block, free nipple graft technique…
- Liposuction “alone”
Mastopexy:
- Techniques: With implants / With fat grafting
Congenital Breast deformities:
- Poland syndrome
- Tuberous breast
- Chest wall deformities: pectus excavatum, pectus carinatum

Small groups of students will have the opportunity to observe live microsurgical techniques in lymphedema treatment.
Live webcast surgery will be shown and interactive participation will be facilitated.
- Lymphedema diagnosis
- Lymphedema conservative treatment
- Managrment of lymphedema complications
- Anatomy and physiology of the lymphatic system
- Assessment and surgical treatment of lymphedema
- Vascularised lymphatic node transfer
- Lympho-venous anastomosis
- Combined surgical treatment for lymhedema
- Lymphangiogenesis and the role of growth factors in lymphedema
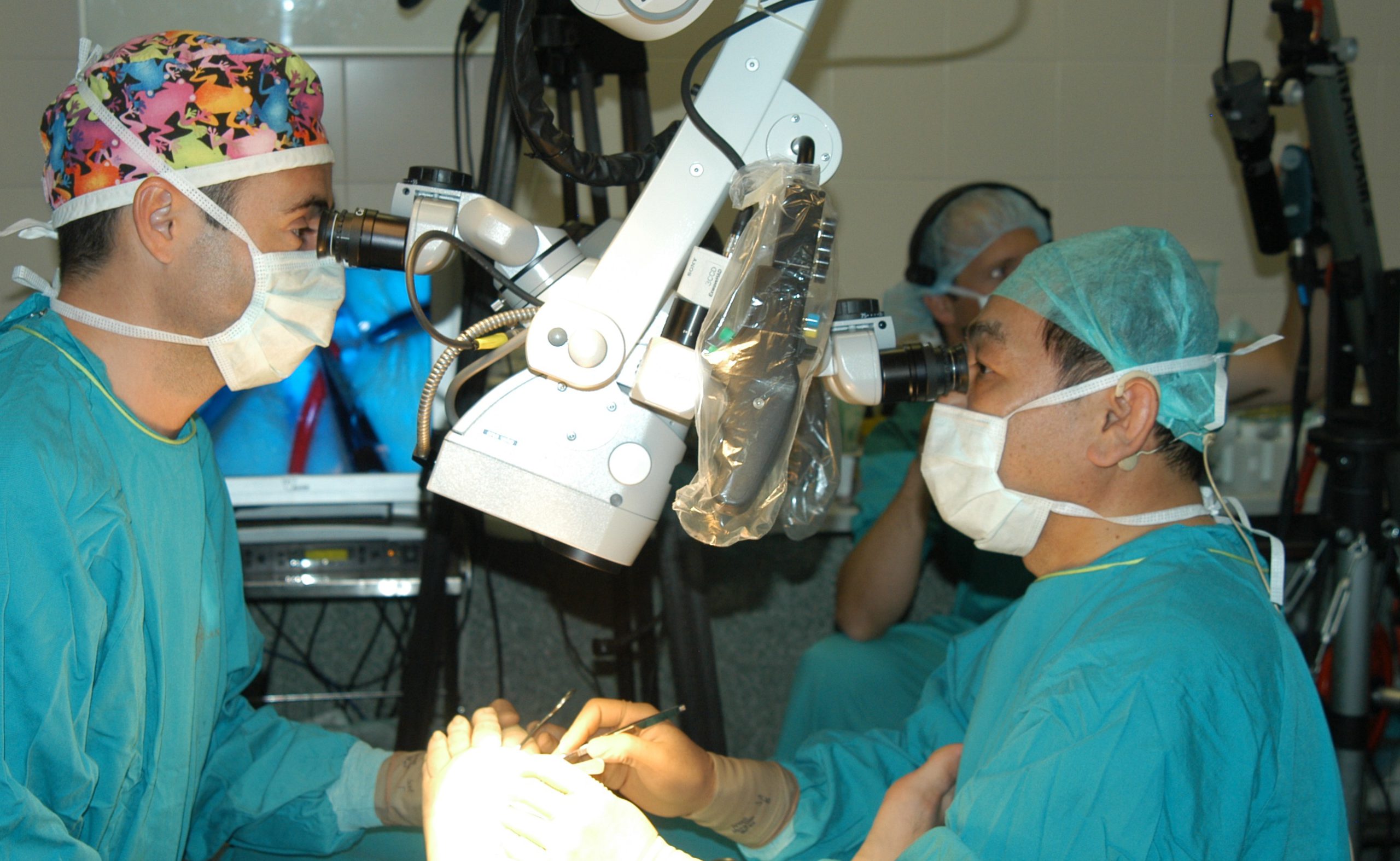
The program includes a practical training module with feedback from facilitators. During this period, students will be involved in clinical cases focused on breast surgery and assist in surgery, following preoperative and postoperative clinics. They will present cases to the other students and faculty to clarify doubts and evaluate the surgery.
From 6 weeks to 12 months before the end of the second year.
- Joint review of the microsurgical technique
- Presentation and discussion of complex clinical cases
- Resolution of immediate and delayed post-surgical complications involving the flaps
- Optimization of technique tailored to each student
On-line.
We need to investigate to produce knowledge that allows us to reduce the impact of health problems, which involves diagnosing and treating diseases better. The clinical research is this inescapable filter where the hypotheses that come from basic research, technological innovation or clinical practices must be tested. But for this applied research activity to be sufficiently valid and useful, we must adequately master the essential conceptual and methodological aspects related to the methodology of clinical research. Making it possible is the objective of this module.
At the end of the module, students will be able to:
- Understand and know how to apply the most important concepts related to clinical research.
- Know how to ask clinical questions of different types and in a structured way.
- Promote the design of the most appropriate clinical studies to answer the clinical questions of interest.
- Conduct searches on scientific publications in a structured, comprehensive and efficient manner.
- Carry out an adequate critical appraisal to identify the strengths and weaknesses of each study.
- Understand and apply the most basic statistical concepts to calculate the different measures of association and effect.
.
Master Thesis
Preparation of a comprehensive written research report is an essential part of a valid research experience, and the student should be aware of this requirement at the outset of the project.
Interim reports may also be required. Sufficient time should be allowed for satisfactory completion of reports, taking into account that initial drafts should be supervised and corrected by your tutor.



